Understanding the Multiple Faces of MoME
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the acronym "MoME" has emerged as a significant term with multiple distinct meanings. While context often clarifies intent, the overlapping nomenclature can create confusion among researchers, practitioners, and enthusiasts alike.
Primary MoME Concepts
Mixture of Matryoshka Experts
A novel AI framework developed by Meta AI and Imperial College London for efficient audio-visual speech recognition.
Meta AI ResearchMixture of Modality Experts
A medical AI model developed by HKUST for non-invasive breast cancer diagnosis using multiparametric MRI.
Medical AIThis comprehensive guide aims to clarify these different meanings, providing researchers and practitioners with a clear understanding of each concept, their applications, and the contexts in which they appear. By examining the technical foundations, development collaborations, and practical implementations, we can better navigate the complex landscape of modern AI research.
MoME in Meta AI: Mixture of Matryoshka Experts
Core Framework and Purpose
The Mixture of Matryoshka Experts (MoME) framework represents a sophisticated approach to enhancing the efficiency and performance of large-scale AI models, specifically in the domain of audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR). This development is a collaborative effort between Imperial College London and Meta AI, along with contributions from NatWest AI Research.
The framework's name, "Matryoshka," is inspired by Russian nesting dolls, aptly describing its ability to handle information at various levels of compression or granularity. This design philosophy enables a single, unified model to operate effectively across different scenarios, from high-fidelity processing to highly compressed processing prioritizing speed and efficiency.
Key Components
- MoE Architecture: Sparse computation with multiple expert sub-networks
- MRL Integration: Hierarchical, multi-scale representation learning
- Shared Router: Consistent expert activation across scales
MoME Architecture Overview
Primary Application: Audio-Visual Speech Recognition
The primary application of MoME is in audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR), a challenging multimodal task that involves transcribing spoken language by simultaneously analyzing both audio signals and visual lip movements.
This dual-modality approach is particularly valuable in noisy environments, where visual cues can significantly improve transcription accuracy and robustness—scenarios where purely audio-based systems often fail.
AVSR Challenges Addressed
- • High computational demands of multimodal processing
- • Sensitivity to input data granularity
- • Resource constraints in real-world deployment
- • Need for dynamic adaptation to varying conditions
Technical Advantages and Performance
Dynamic Capacity Allocation
Sparse MoE architecture activates only a small subset of experts for each input, significantly reducing computational load.
State-of-the-Art Performance
Achieves SOTA performance on LRS2 and LRS3 datasets for AVSR, ASR, and VSR tasks with fewer active parameters.
Resource Efficiency
Addresses computational inefficiency in large models through elastic inference and cross-scale knowledge transfer.
"MoME requires significantly fewer parameters during inference than competing baselines, making deployment feasible on a wider range of hardware, including devices with limited computational resources."
Development and Collaboration

Multi-Institutional Partnership
The development of MoME is a testament to collaborative research excellence, bringing together the academic prowess of Imperial College London and the industrial research capabilities of Meta AI, with contributions from NatWest AI Research.
The research paper, titled "MoME: Mixture of Matryoshka Experts for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition," has been submitted for presentation at NeurIPS 2025, underscoring its scientific significance.
Key Institutions
Imperial College London
iBUG team specializing in multimodal signal processing
Meta AI
Industrial-scale AI research and development
NatWest AI Research
Practical applications in financial services
Important Distinction
While MoME is a significant project within the Meta AI ecosystem, it is distinct from other major projects like the LLaMA series, though they may share some architectural principles such as Mixture-of-Experts.
MoME vs LLaMA 4 Comparison
| Feature | MoME (Meta AI) | LLaMA 4 (Meta AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Mixture of Matryoshka Experts | Large Language Model Meta AI 4 |
| Primary Goal | Efficient, adaptable model for AVSR | General-purpose foundational model |
| Key Innovation | Integration of MoE with MRL | MoE architecture for scalability |
| Core Application | Audio-Visual Speech Recognition | Wide range of NLP tasks |
The Broader "MoME" Landscape
Mixture of Modality Experts (MOME)
Medical AI Innovation
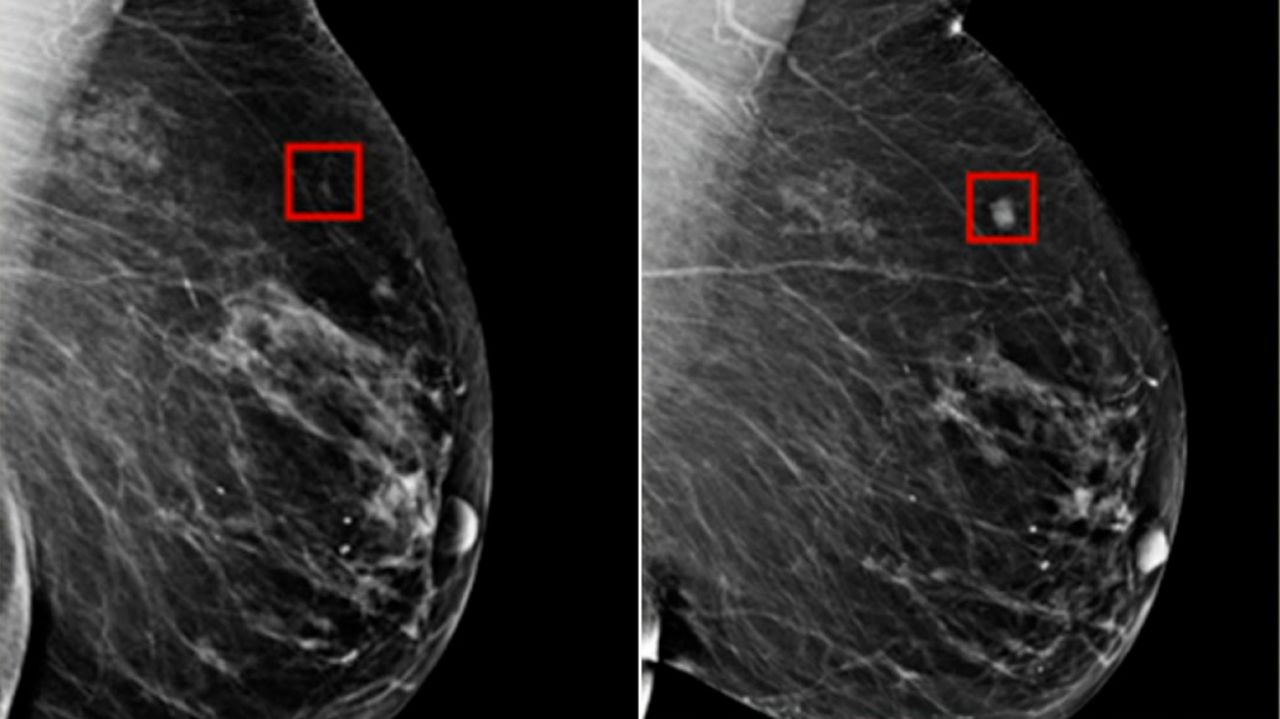
In a completely different domain, Mixture of Modality Experts (MOME) refers to a groundbreaking AI model developed by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) for non-invasive breast cancer diagnosis.
This model leverages a mixture-of-experts framework and transformer architecture to effectively fuse information from multiple imaging modalities, specifically multiparametric MRI (mpMRI), achieving expert-level accuracy comparable to experienced radiologists.
Key Applications
- Tumor Malignancy Classification: Expert-level accuracy in cancer detection
- Molecular Subtyping: Advanced tumor characterization
- Treatment Response Prediction: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy outcomes
- Non-Invasive Diagnosis: Reduced need for invasive biopsies
Critical Distinction
This MOME model is entirely distinct and unrelated to the Mixture of Matryoshka Experts framework developed in collaboration with Meta AI. They are separate research initiatives with different goals, developers, and underlying technologies.
Technical Implementation
Data Scale
China's largest mpMRI breast cancer dataset for training and validation
Architecture
Transformer-based MoE framework for multimodal fusion
Collaboration
Multi-institutional partnership including medical institutions
Other Variants and Related Concepts
Beyond the two primary meanings of "MoME," the AI research landscape includes other related concepts and variations that leverage similar naming conventions or share underlying principles. Understanding these related ideas provides a comprehensive view of the field.
Summary of MoME and Related Concepts
| Concept Name | Developer / Research Group | Primary Focus / Application | Key Innovation / Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture of Matryoshka Experts (MoME) | Meta AI & Imperial College London | Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) | Integration of MoE with MRL for dynamic, multi-scale processing |
| Mixture of Modality Experts (MOME) | Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) | Non-invasive breast cancer diagnosis | Fusing information from multiple medical imaging modalities (mpMRI) |
| Mixture of Multimodal Experts (MoME) | General research concept | Enhancing generalist Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) | Combining MoVE and MoLE to mitigate task interference |
| Mixture of a Million Experts (MoME) | General research concept | Exploring extreme scaling of MoE architectures | Investigating massive numbers of highly specialized experts |
| Matryoshka Mixture-of-Experts (M-MoE) | General research concept | Enabling elastic inference in MoE models | Coarse-to-fine expert ranking for dynamic adjustment |
Mixture of Multimodal Experts
A framework designed to enhance generalist Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by addressing task interference through specialized expert systems.
Mixture of a Million Experts
An ambitious research direction exploring extreme scaling of MoE architectures to achieve finer-grained specialization.
Matryoshka Mixture-of-Experts
A training framework enabling elastic inference in MoE models through systematic variation of activated experts during training.
The Foundational Architecture: Mixture of Experts (MoE)
The Mixture of Experts (MoE) is a foundational architectural concept in deep learning that has gained significant traction in recent years, particularly in the development of large-scale AI models. The core idea is to create models with very large capacity but with computational costs that don't scale linearly with the number of parameters.
Core Principles of MoE
Sparse Model Architecture
The cornerstone of MoE is its sparse model design, which departs from traditional dense architectures where all parameters are active for every computation. Instead, MoE uses multiple smaller, independent neural networks called "experts."
For any given input, only a small subset of experts is selected to participate in the computation, while the rest remain inactive. This selective activation decouples the model's capacity from its computational cost.
Key Benefits
- • Larger model capacity without proportional computational increase
- • Modular design enabling specialized expert training
- • Efficient resource utilization during inference
Gating Network and Expert Routing
The gating network acts as the "brain" of the MoE model, making intelligent decisions about which experts to activate for each input. This dynamic routing mechanism gives MoE its adaptability and efficiency.
MoE Architecture
Routing Process
- 1. Input data passes through gating network
- 2. Network produces relevance scores for each expert
- 3. Top-k experts selected based on highest scores
- 4. Selected experts process the input
- 5. Outputs combined using weighted sum
MoE in Meta AI's Ecosystem
The Mixture of Experts architecture has become integral to Meta AI's strategy for developing large-scale, efficient, and powerful AI models. This adoption allows Meta to build high-capacity models while keeping computational and energy costs manageable—a crucial consideration for deployment across Meta's vast product ecosystem.
Strategic Advantages
- • High capacity with manageable costs
- • Scalable across multiple products
- • Efficient resource utilization
- • Modular architecture for specialization
Application Areas
- • Content recommendation systems
- • Feed ranking algorithms
- • AI assistants and chatbots
- • Virtual reality experiences

"The use of MoE is a key enabler of Meta's vision, providing a practical path to scaling up AI capabilities across billions of users."
Adoption in the LLaMA 4 Model Series
The LLaMA 4 model series prominently features the Mixture of Experts architecture as a key design element. This strategic move creates models that are both highly capable and computationally efficient.
LLaMA 4 Scout
LLaMA 4 Maverick
Note: This design allows these models to have a very large total number of parameters while maintaining a much lower active parameter count during inference, making them more practical to deploy and use.
Comparative Analysis
MoME Concepts Comparison Matrix
| Concept | Developer | Primary Domain | Key Innovation | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture of Matryoshka Experts | Meta AI & Imperial College | Audio-Visual Processing | MoE + MRL Integration | Research (NeurIPS 2025) |
| Mixture of Modality Experts | HKUST | Medical Imaging | Multiparametric MRI Fusion | Clinical Application |
| Mixture of Multimodal Experts | General Research | Multimodal LLMs | Task Interference Mitigation | Conceptual |
| Mixture of a Million Experts | General Research | Extreme Scaling | Massive Expert Specialization | Theoretical |
| Matryoshka Mixture-of-Experts | General Research | Elastic Inference | Dynamic Expert Activation | Active Research |
Key Insights
- Nomenclature Overlap: The "MoME" acronym spans multiple distinct domains, from speech recognition to medical diagnostics
- Shared Foundations: All concepts build upon the core Mixture-of-Experts architecture with specialized innovations
- Context Dependency: Proper understanding requires awareness of the specific research domain and application context
Research Implications
- Literature Review: Researchers must carefully distinguish between different MoME concepts when reviewing literature
- Citation Accuracy: Proper attribution requires understanding the specific MoME variant being referenced
- Innovation Building: New research can benefit from cross-pollination between different MoME implementations
Conclusion
The acronym "MoME" represents a fascinating case study in the evolution of artificial intelligence terminology, where multiple distinct concepts have converged under similar naming conventions while maintaining their unique identities and applications.
Key Takeaways
Primary MoME Concepts
- Meta AI's MoME: Mixture of Matryoshka Experts for audio-visual speech recognition, combining MoE with MRL for dynamic multi-scale processing
- HKUST's MOME: Mixture of Modality Experts for non-invasive breast cancer diagnosis using multiparametric MRI fusion
Broader Landscape
- Related Concepts: Multiple variants exploring different aspects of expert architectures and multimodal processing
- Foundation: All build upon the core Mixture-of-Experts architecture with specialized innovations
This comprehensive analysis reveals that while the "MoME" acronym may appear in different contexts, each implementation serves distinct purposes and addresses unique challenges within the AI landscape. The Meta AI-Imperial College collaboration focuses on efficient multimodal processing for speech recognition, while HKUST's work targets critical healthcare applications.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for researchers, practitioners, and enthusiasts navigating the complex terminology of modern AI. As the field continues to evolve, clear communication and precise terminology will remain essential for advancing knowledge and avoiding confusion.
Future Directions
As AI research continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in expert-based architectures and multimodal processing. The success of current MoME implementations suggests promising directions for:
Enhanced multimodal fusion techniques
More efficient expert routing mechanisms
Expanded medical AI applications
讨论回复
0 条回复还没有人回复
