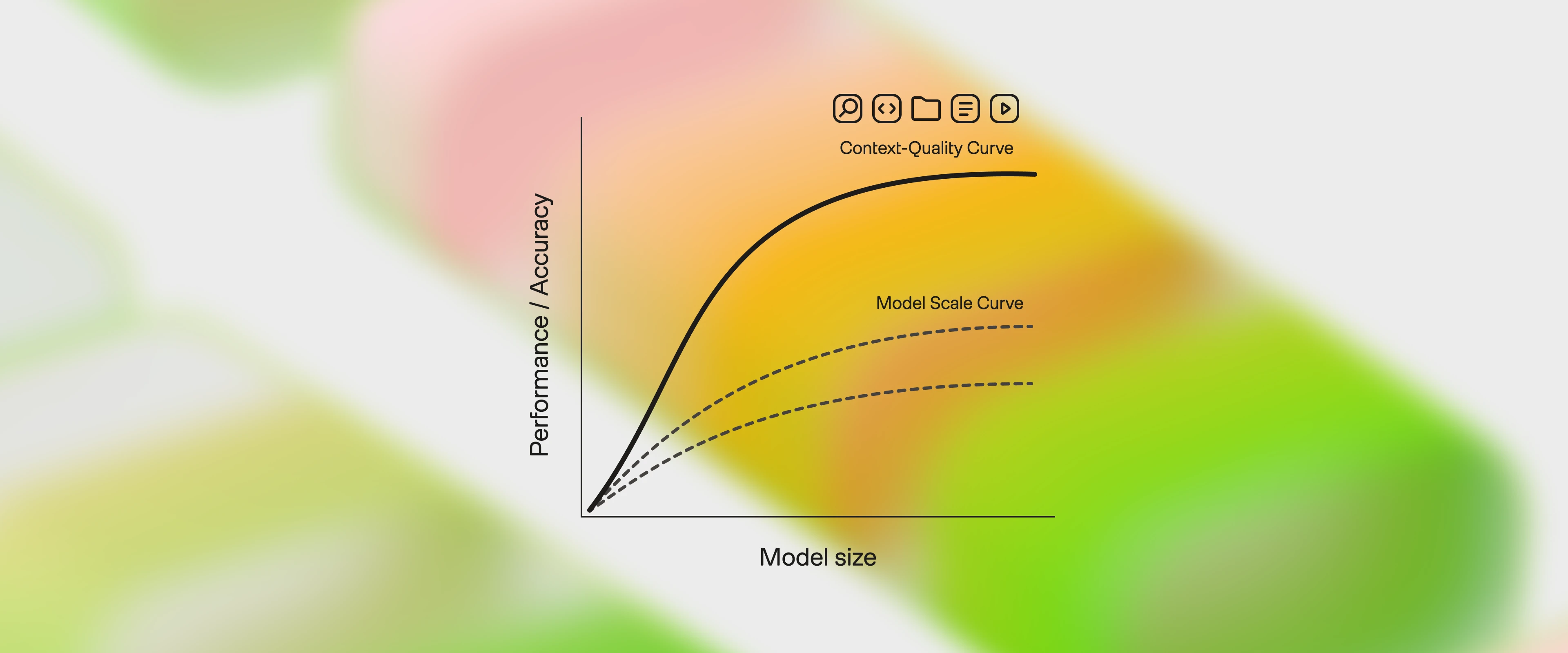
Large Language Model applications increasingly rely on context adaptation rather than weight updates. Current approaches suffer from two critical limitations:
Brevity bias: Over-prioritizing concise summaries at the expense of detailed domain insights
Context collapse: Iterative rewriting erodes details over time, leading to performance drops
ACE treats contexts as evolving playbooks that accumulate, refine, and organize strategies through a modular process.