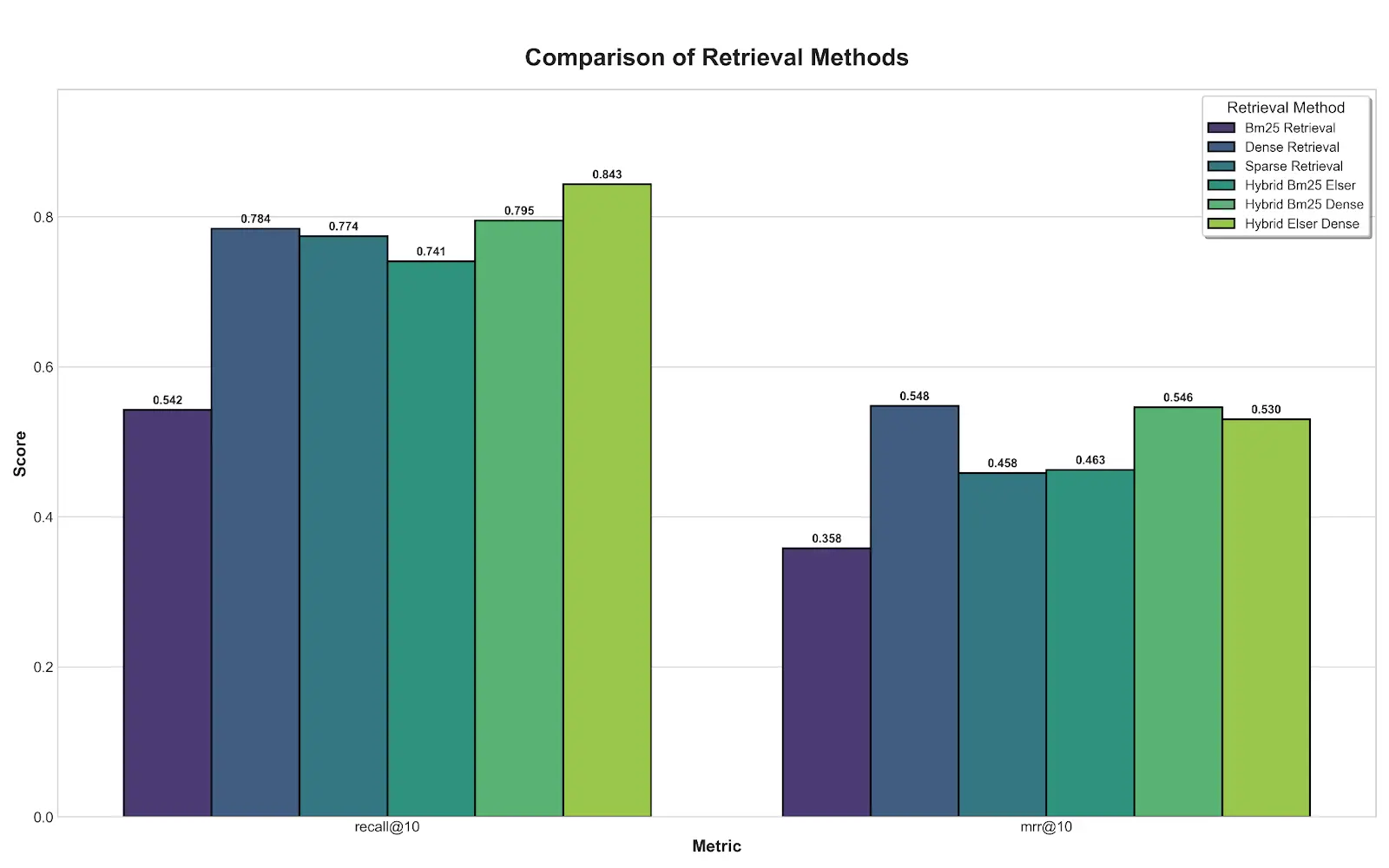
- Modern long-context LLMs perform well on synthetic "needle-in-a-haystack" (NIAH) benchmarks
- These tests overlook how noisy contexts arise from biased retrieval and agentic workflows
- Need for more realistic evaluation that captures real-world factors

Traditional needle-in-a-haystack evaluation